LEDs take up for about 40% to 70% of the cost of an LED display. The significant reduction in the cost of LED display screens is due to the reduction in the cost of LEDs. The quality of LED packaging has a great impact on the quality of LED display screens. The key to packaging reliability includes the selection of LED chips, packaging materials, and manufacturing technique. In addition, strict reliability standards are also the key to high-quality LEDs.

Kinglight 2727 RGB LED
As LED displays gradually penetrate the high-end market, the quality requirements for LEDs are getting higher and higher. Here in this article, we’ll discuss the key technologies for achieving high-quality LEDs based on the actual experience of high-quality LED display packaging process.
SMD stands for Surface Mounted Devices, which means surface mounted LEDs, mainly PCB structure LEDs (Chip LEDs) and PLCC structure LEDs (TOP LEDs). Below, we will take PLCC structure TOP LEDs as an example to explore the impact of LED packaging on the quality of LED screens.
Generally speaking, the main materials used for LED display device packaging include brackets, LED chips, die attach glue, bonding wires and packaging glue.
A frame is where the LED chips housed and protected.
1) The role of the frame
The PLCC (Plastic Leaded Chip Carrier) bracket is the carrier of the SMD LED device and plays a key role in the reliability and light output performance of the LED.
2) Production process of the frame
The production process of the PLCC bracket mainly includes metal strip punching, electroplating, PPA (polyphthalamide) injection molding, bending, five-sided three-dimensional inkjet and other processes. Among them, electroplating, metal substrate, plastic materials, etc. account for the main cost of the bracket.
3) Improved structure design of the frame
Since the PPA and metal of the PLCC bracket are physically bonded, the gap will become larger after the high temperature reflow furnace, which makes it easy for water vapor to enter the device along the metal channel, thus affecting reliability.
For example, Kinglight LEDs for outdoor displays adopt designs such as stretch cups and multi-waterproof structures to improve the waterproof performance of LEDs. Tests have shown that the stretch cup can greatly improve the airtightness of LEDs and extend the path for water vapor to enter the device, thereby effectively reducing the impact of water vapor intrusion on product performance.
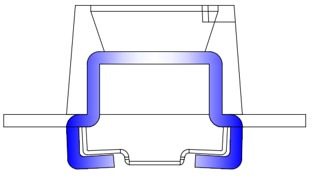
Kinglight LEDs for outdoor application utilize stretched cup design to prevent moisture penetration
Know more about Kinglight LEDs for outdoor display, please click >>>
LED chips are the core component of an LED, and their reliability determines the lifespan and luminous performance of LEDs and also the entire LED display. The cost of LED chips accounts for the largest proportion of the total cost of LED devices. As the manufacturing costs decrease, the size of LED chips become smaller and smaller, which also brings a series of reliability problems.
As the size decreases, the pads of the P electrode and N electrode on the LED chip also decrease. The reduction of the electrode pad directly affects the quality of the welding wire, which is easy to cause the gold ball to detach or even the electrode itself to detach during the packaging process and use, and eventually fail. At the same time, the distance a between the two pads will also decrease, which will cause the current density at the electrode to increase excessively, and the current will gather locally at the electrode. The unevenly distributed current seriously affects the performance of the chip, causing the chip to have problems such as excessively high local temperature, uneven brightness, easy leakage, electrode drop, and even low luminous efficiency, which ultimately leads to reduced reliability of LED displays.
Bonding wire is one of the key materials for LED packaging. Its function is to realize the electrical connection between the chip and the pin, and it plays the role of current introduction and extraction between the chip and the outside world. Commonly used bonding wires for LED device packaging include gold wire, copper wire, palladium-plated copper wire and alloy wire.
1) Gold wire
Gold wire is the most widely used and has the most mature process, but it is expensive, resulting in excessively high LED packaging costs.
Kinglight A series LEDs adopt gold wires for more stable electrical connection
2) Copper wire
Copper wire has the advantages of being cheap, having good heat dissipation effect, and slow growth of intermetallic compounds during wire bonding. The disadvantages are that copper is easy to oxidize, has high hardness and high strain strength. Especially in the heating environment of the copper ball bonding process, the copper surface is very easy to oxidize, and the oxide film formed reduces the bonding performance of the copper wire, which puts higher requirements on process control in the actual production process.
3) Palladium-plated copper wire
In order to prevent copper wire oxidation, palladium-plated bonding copper wire has gradually attracted attention in the packaging industry. Palladium-plated bonding copper wire has the advantages of high mechanical strength, moderate hardness, and good welding balling, which is very suitable for high-density, multi-pin integrated circuit packaging.
At present, there are two common options for the glue used to encapsulate LEDs, including epoxy resin and silicone.
1) Epoxy resin
Epoxy resin is easy to age, susceptible to moisture, has poor heat resistance, and is easy to change color under short-wave light and high temperature. It has certain toxicity in the gel state. The thermal stress is not very compatible with the LED, which will affect the reliability and life of the LED. Therefore, epoxy resin is usually attacked for enhanced performance during LED packaging process.
2) Silicone
Compared with epoxy resin, silicone has a higher cost-effectiveness, excellent insulation, dielectric and adhesion. But the disadvantage is that it has poor airtightness and is easy to absorb moisture. Therefore, it is rarely used in the packaging application of LEDs.
In addition, high-quality LED displays also have special requirements for display effects. For example, Kinglight utilizes additives to reduce the stress of the glue and achieve a matte effect, thereby effectively reducing possible bonding wire breakage inside the module and decreasing the reflectivity of the LED surface.
Related Reading:
LED Packaging Structure, Process Development Status And Trends >>>
Everything about LED packaging >>>
LED Package: Popular Technologies and Differences >>>