When look at an object from the front and side, usually we get obvious visual differences. Similarly, when we watch at an LED screen from different angles, there are often some subtle but imperceptible differences. Once this difference at a certain viewing angle has a more obvious impact on the image quality of the LED screen, it can be easily captured by our naked eyes and leads to a decrease in the viewing experience, indicating that this viewing angle has exceeded the maximum viewing angle of the LED screen.
LED display
So, what is LED screen viewing angle? What factors would affect it? For different LED packaging technologies such as SMD LED, DIP LED and COB LED, are there differences over the viewing angle of the screen? Here in this article, we’ll provide a comprehensive guide over these questions, and wish you can understand better about LED screen viewing angle.
LED screen viewing angle refers to the angle at which we can acquire clear images on an LED screen without quality degradation, which means no visible color offset or brightness deviation from the original images. And in addition, LED screen viewing angles include two aspects, both horizontal and vertical.
The horizontal viewing angle refers to the angle range within which we can still normally view the image within a certain angle to the left or right from the vertical normal of the display (the vertical imaginary line in the middle of the display).
The vertical viewing angle is the viewing angle upward or downward based on the horizontal normal of the display.
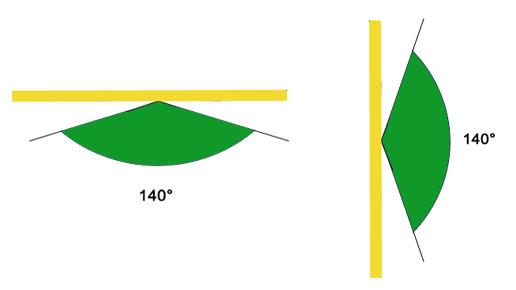
LED screen horizontal and vertical viewing angle
The packaging method of the LED chips usually decides the viewing angles of LED screens.
Different packaging technologies will affect the divergence angle of the light emitted by LEDs, thereby affecting the viewing angle of an LED screen.
In theory, the larger the viewing angle, the wider the range that we can watch an LED screen, but it may also cause the screen brightness to decrease. For different application scenarios, such as indoor and outdoor LED displays, the requirements for viewing angles are also different. Usually, indoor displays require a viewing angle of more than 120°, while outdoor displays require a viewing angle of more than 140°.
So how can we measure out the viewing angles of an LED screen?
The answer is the contrast of the screen. When the viewing angle increases, the contrast of the displayed image will gradually decrease. When the contrast drops to 10:1, this angle is the maximum viewing angle of the LED display.
Therefore, the optimization of the viewing angle is actually the pursuit of the best balance between contrast and viewing angle.
The viewing angle of an LED display is related to many factors, including the packaging method of LED chips, viewing angle and distance, pixel density, LED arrangement, brightness, LED display module and manufacturing process, ambient light intensity, panel design, surface treatment technology, and the sophistication of the manufacturing process.
LED chip packaging method: The range of the viewing angle is mainly determined by the packaging method of the LED chips. Different packaging technologies will result in different light scattering angles, which will affect the viewing angle.
Pixel density: The higher the pixel density, the audience can still clearly identify the image at a larger viewing angle.
LED arrangement: Different LED arrangements will affect the viewing angle. For example, the LED arrangement following SMD packaging rules usually has a wider viewing angle.
Brightness: There is a certain trade-off between brightness and viewing angle. The higher the brightness, the more light scattering and refraction may increase, resulting in a smaller viewing angle.
LED module and manufacturing process: High-quality LED modules and sophisticated manufacturing processes can provide a wider viewing angle. Manufacturers can improve the viewing angle of the display by optimizing the optical design and reducing light scattering and reflection.
Ambient light intensity: When used outdoors, strong ambient light may cause the image brightness of full-color LED display screens to be insufficient and a loss of viewing angles. Proper measures to protect the screen from direct sunshine are essential to provide a wider viewing angle.
Panel design: Different panel designs determine the way and range of light scattering on the screen. For example, some advanced LED screens adopt a wide-angle design, which optimizes the propagation path of light so that a clear picture can still be maintained at a larger angle.
Surface treatment technology: Some screens use special coatings or surface treatment technologies, which can effectively reduce the reflection and scattering of light and improve the contrast and clarity of the picture. This treatment technology enables the LED screen to maintain high brightness and color reproduction at a larger viewing angle.
The sophistication of the manufacturing process: The sophistication of the manufacturing process will also affect the viewing angle. Some manufacturers will reduce the scattering and reflection of light by optimizing the optical design to improve the viewing angle of the LED screen.
It can be seen that the viewing angle of the LED display is the result of the combined effect of multiple factors. By optimizing these factors, the viewing angle of the display can be improved, thereby enhancing the audience’s viewing experience.
As we all know, there are different technologies in the manufacturing of LED screens, such as SMD LED, DIP LED, and COB LED. So are there any differences of the viewing angles between these different LED technologies?
Of course, SMD, DIP and COB LEDs offer different features over their viewing angles.
SMD LED
SMD LED usually has a wider viewing angle and more uniform color performance.
SMD LED technology allows multiple LED chips to be integrated into one package, which increases pixel density and is suitable for high-definition display. The viewing angle of SMD LED displays is usually around 140°, which allows viewers to view screen content from a wider angle while maintaining good color performance and image quality.
Kinglight SMD LEDs ensure wide viewing angle for your LED screen
DIP LED
DIP LED offers relatively narrow viewing angles, generally between 100-110°.
The LEDs of DIP (dual in-line package) displays are made by wave soldering. In the early days, the red, green and blue LEDs were inserted on the PCB to form an RGB pixel. Due to the complex production organization of DIP displays, it is not easy to implement mechanized production and the production efficiency is low, so the viewing angle is not as wide as SMD and COB displays.
COB LED
COB LED allows the largest viewing angles among the three different LED technologies, reaching 160° or even higher.
COB (chip on board) technology packages the LED chips directly on the PCB board and then encapsulates it with epoxy resin to form a module. This packaging method does not require mask protection, and the left and right viewing angles are increased, providing a wider viewing angle, allowing us to view screen content from a wider angle while maintaining good image quality.
In summary, SMD LED displays provide a wider viewing angle and uniform color performance, while COB LED displays provide the widest viewing angle, suitable for application scenarios that require a wide viewing angle. The viewing angle of DIP LED displays is relatively narrow, suitable for specific application requirements.