After years of development, conventional common anode LED displays have formed a stable industrial chain, driving the popularity of LED screens. However, they also have the disadvantages of high screen temperature and excessive power consumption. Common cathode LED displays emerge and have attracted great attention in the LED screen market due to their energy saving features. Common cathode LED displays can achieve energy savings of up to 75%. So, what are common cathode LED displays? What are the advantages of common cathode LED displays?

“Common cathode” means common cathode design utilized in an LED display to power its LED pixels. Common cathode design allows to power the R, G, B (red, green, blue) lamp beads inside the LED module separately and accurately according to the different optimal operating voltages and currents required by R, G, and B (red, green, and blue) lamp beads. In a common cathode LED, the current will first pass through the lamp beads and then to the negative electrode of the IC, and the forward voltage drop will be reduced, resulting in the internal resistance will become smaller. Hence, common cathode design is an energy saving solution for LED displays.
1). Different ways to power LED pixels
In the common cathode power supply method, current first passes through the lamp bead and then to the negative electrode of the IC, making the forward voltage drop smaller and the conduction internal resistance also smaller.
The common anode is the current flowing from the PCB board to the lamp bead, supplying unified power to R, G, B (red, green, blue), which causes the forward voltage drop of the circuit to increase.
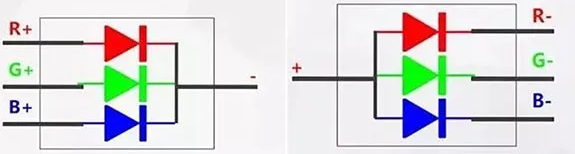
Common cathode VS common anode LED display
2). Different voltage input
Common cathode design inputs current and voltage to R, G, B (red, red, blue) individually. Red, green and blue lamp beads have different voltage requirements. The voltage of red lamp beads is required to be around 2.8V, and the voltage of green and blue lamp beads is required to be around 3.8V. Such power supply can achieve accurate power supply with low power consumption, and the heat generated by the LED display during operation will be much lower.
The common anode provides a unified power supply to R, G, and B (red, green, and blue) with a voltage higher than 3.8V (such as 5V). At this time, the voltages obtained by red, green, and blue are all unified 5V, but the optimal working voltage required by the three lamp beads of red, green, and blue is much lower than 5V. According to the power formula P=UI, when the current remains unchanged, the higher the voltage, the higher the power, which means the greater the power consumption; at the same time, the LED display will also generate more heat during operation.
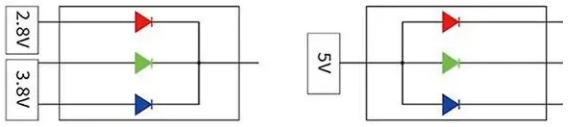
Voltage inputs of common cathode LED & common anode LED
Common cathode LED display generates less heat during operation. It’s tested at the same circumstances, an common cathode LED display is about 20 degrees centigrade lower than a conventional common anode LED display with the same specifications. Meanwhile, its power consumption is 50% lower than that of a conventional common anode LED display.
High screen temperature is always a factor affecting the service life of an LED display. And common cathode design is no doubt a better solution for LED display and for our green planet.
1). Accurate power allocation and energy saving
Common cathode LED displays adopt precise voltage input based on the different optoelectronic characteristics of the three primary colors of LED red, green and blue. Equipped with an intelligent IC, the display control system accurately allocate different voltages to the LED and drive circuit, making the common cathode LED display consumes about 40% less power than conventional common anode LED display.
2). Long time vivid color display
The common cathode LED display can accurately control the voltage, which not only reduces power consumption, but also reduces heat generation. The decreased screen heat assures no wavelength drift at long time operation, which result in stable display of vivid colors.
3). Longer life span
Meanwhile, less screen heat also effectively reducing the probability of LED damage, improving the stability and reliability of the entire display system, and greatly extending the life span of a common cathode LED display.
Kinglight LEDs with “N” in their product IDs are common cathode LEDs for less power consumptions, such as the 1820N-A2 LED.
Supporting equipment related to common cathode LED display technology, such as LEDs, power supplies, driver ICs, etc., are currently not as mature as the common anode LED display industry chain. In addition, the current series of common cathode ICs is incomplete, and the overall volume is not large, while common anode LED displays still take up 80% of the LED display market.
The current slow advancement of common cathode technology is mainly due to high production costs. Based on the original supply chain collaboration relationship, common cathode requires customized cooperation from all ends of the industry chain such as chips, packaging, and PCB, which is costly.
In this era of extremely high calls for energy conservation, the emergence of common cathode transparent LED screens has undoubtedly become the support point for this industry to pursue. However, there is still a long way to go to achieve comprehensive promotion and application in a larger sense, which requires the joint efforts of the entire industry. As a development trend of energy conservation, common cathode LED displays involve power usage and operating costs. Therefore, energy conservation is related to the interests of LED display operators and the use of national energy.
In fact, common cathode LED displays don’t increase the cost much compared to conventional common anode LED displays; but in the long run, common cathode LED displays win for energy saving and less screen heat features.