LED technology has changed our way of displaying, from single color LED sings to large RGB LED displays with millions of pixels. Since LED display technology keeps evolving, the application scenarios expend into every corner of our lives. So how many types of LED displays are there? What are the differences? Let’s go and dive into the world of LED displays.

LED, abbreviation for light emitting diode, is a semiconductor material that emits light when current passes through it. A diode, allowing current to flow in one direction, features the electronic with energy efficient and long lasting performance. This makes LEDs a perfect choice for displays.
There are different definitions over LED displays, some focusing on the content they displays, while others emphasizing on the usage and purpose. So they’re a lot of different names for different type definition of LED displays.
When we define LED display types over the content they display, then we have below types of LED displays.
1-1. Text LED display
Text LED displays, just as the implied, are designed to display plain text including letters and numbers. They’re commonly seen in front of restaurants, such as a welcome board saying “Welcome”, “We’re Open”, or “We’re Closed”.
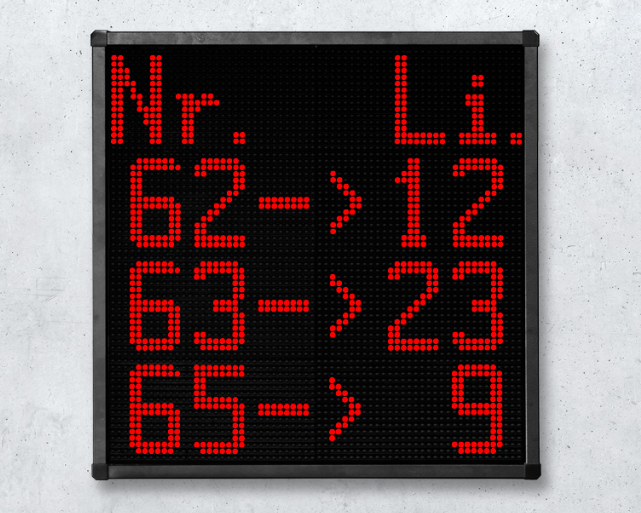
1-2. Numeric LED display
Unlike text LED display, a numeric LED display only displays numbers, and usually in single colors like red, yellow, green, etc. It is usually used to display phone numbers.
1-3. Image LED display
Image LED displays are more sophisticated than text LED displays and are designed to display stationary images. And of course, they’re able to display text too.
1-4. Video LED display
A video LED display is often called as LED video wall. LED video walls can be widely seen at shopping malls, control rooms, transition hubs, conferences, concerts, and events.
2-1. Rental LED display
Rental LED displays indicate displays being rent for temporary uses. This type of LED display usually features slim design, seamless splicing, and easy disassembly and re-installation. Also, anti-bump performance is a must for these LED screens to avoid damages while frequent transportation and re-installation.
2-2. Fixed LED display
Fixed LED display is a type of display being fixedly installed at certain places, for example, on the facade of shopping centers, standing at the traffic conjunctions. Fixed LED display usually operates day and night. Thus, power efficiency is necessary to reduce the cost for the owner.
2-3. Fine pitch LED display
Fine pitch LED display describes LED display with smaller pixel pitch, usually under 2.5mm. That means the space between adjacent pixels of the display is less than 2.5mm.
The smaller pixel pitch is, the more pixels the screen has in the same dimensions.
Fine pitch LED display is usually used for high definition displaying of high quality images and videos. Since fine pitch LED display has rich details and is more suitable for watching at a short distance, it’s usually used indoors to grab more attention with delivering quality content to the audiences.
Kinglight provides a wide variety of LEDs for different types of LED displays
Indoor or outdoor LED display is another way that we define an LED display being used either indoors or outdoors.
For an indoor LED display, it requires less for weather resistant features and usually less brightness than an outdoor LED display, but usually higher resolution than an outdoor LED display for much shorter viewing distance.
For an outdoor LED display, waterproof and weather resistant performance are necessary. And of course, high brightness is needed to withstand strong outdoor light.
When we mention synchronous or asynchronous LED display, it means how we control the LED display.
Synchronous LED Display:
A synchronous LED display refers to a display system where all the LED panels are connected to a central control system, and the content is updated and synchronized in real-time across all panels simultaneously. The control system ensures that the content and timing of the display are precisely coordinated across all panels, resulting in a unified and consistent visual output. Synchronous LED displays are commonly used in situations where multiple panels need to display the same content, such as large-scale video walls or displays in stadiums, stages, and public spaces.
Asynchronous LED Display:
An asynchronous LED display, also known as a standalone LED display, operates independently without requiring a continuous connection to a central control system. Each LED panel in an asynchronous display has its own built-in control system and memory storage, allowing it to operate autonomously. Content is pre-programmed or uploaded to the individual panels in advance, and each panel displays its assigned content without relying on real-time synchronization with other panels. Asynchronous LED displays are typically used in situations where different panels need to display different content or when real-time control is not necessary. They are commonly found in retail stores, restaurants, transportation hubs, and other environments where targeted messaging or localized content is desired.
5-1. Flexible LED display
Flexible LED display is a type of LED display utilizing soft PCB and rubber material for bendable features. Flexible LED display can achieve creative designs like curved, wave-like, circular, and spherical shapes.
5-2. Transparent LED display
Transparent LED display utilizes LEDs projecting light onto transparent surface to produce images on both sides.The transparency of a transparent LED display is usually between 70% and 90%.
5-3. 3D LED display
3D LED display usually means glasses free 3D LED display. This type of LED display usually has an L shaped structure composed by two flat LED displays in 90 degrees.
It’s also named as naked-eye 3D LED display. It utilizes the principle how we humans see 3D images in our eyes. There are slight differences of the images being displayed on the two flat LED displays, which can be observed by the left and right eyes and form 3D images in our brain.
LED displays are often described with some popular names, for example, LED signage, LED billboard, LED scoreboard, LED poster, etc.
LED Poster:
An LED poster is a compact and portable display that typically resembles a traditional printed poster. It is characterized by its slim design, lightweight construction, and ease of installation. LED posters are commonly used in indoor environments like retail stores, shopping malls, exhibitions, and events. They are suitable for displaying advertisements, product promotions, and informational content.
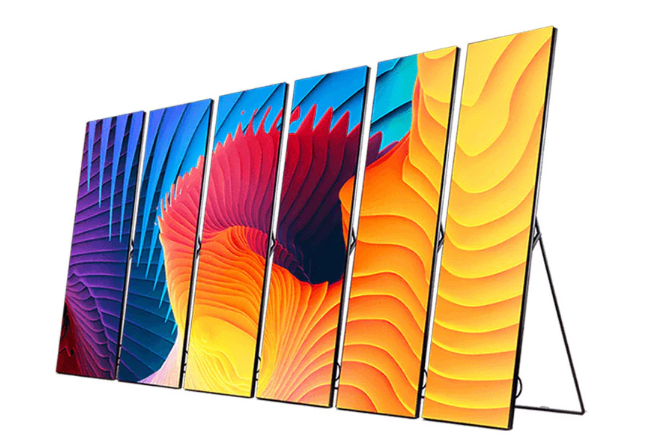

LED poster
LED Signage:
LED signage refers to a broader category of LED displays used for various purposes. LED signage comes in different forms, including single-line LED signs, LED video walls, and LED display panels. LED signage is often used for informational and promotional purposes in both indoor and outdoor settings. It can be utilized for displaying text, graphics, animations, and videos. LED signage is commonly seen in retail stores, airports, stadiums, hotels, transportation hubs, and corporate buildings.
LED Billboard:
LED billboards are large-format outdoor displays designed for high visibility and long-range viewing. They are significantly larger than LED posters and LED signage. LED billboards are often installed alongside highways, busy roads, and in densely populated areas to capture the attention of a wide audience. They are capable of displaying dynamic content, including advertisements, videos, and animations. LED billboards are known for their high brightness, weather resistance, and the ability to deliver impactful visual messages.

LED billboard
LED Scoreboard:
An LED scoreboard is a specialized type of LED display used primarily in sports stadiums and arenas to provide real-time scoring and game information to spectators. LED scoreboards are designed to deliver clear and easily readable information, even from a distance.
Behind LED displays, there are several different LED display technologies available, each with its own characteristics and applications. Here are some of the commonly used LED display technologies.
DIP (Dual In-Line Package) LED:
DIP LEDs are traditional LED packages with individual diodes mounted on a circuit board. They are known for their robustness and high brightness capabilities. DIP LEDs are commonly used in outdoor displays and large-format LED screens.
SMD (Surface-Mount Device) LED:
SMD LEDs are smaller and more compact than DIP LEDs. They are mounted directly onto the surface of a circuit board, allowing for higher pixel densities and improved image quality. SMD LEDs are commonly used in both indoor and outdoor LED displays, including video walls and digital signage.
COB (Chip-on-Board) LED:
COB LEDs feature multiple LED chips directly mounted onto a circuit board, creating a densely packed array of LEDs. COB technology provides enhanced brightness and color uniformity. COB LEDs are commonly used in indoor displays and small-sized LED screens.
MicroLED technology utilizes tiny individual LED pixels that are typically smaller than 100 micrometers. MicroLED displays offer high resolution, exceptional brightness, and excellent color reproduction. They are often used in high-end applications such as large-format displays, video walls, and virtual reality headsets.
OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode):
OLED displays use organic compounds that emit light when an electric current is applied. OLED technology offers several advantages, including high contrast, wide viewing angles, and excellent color reproduction. OLED displays are commonly used in small-sized screens like smartphones, tablets, and wearable devices.
Mini-LED:
Mini-LED technology is a variant of traditional LED displays that incorporates smaller LED chips, typically less than 200 micrometers. Mini-LED displays can provide improved contrast, higher brightness levels, and better color reproduction compared to standard LED displays. They are commonly used in high-end TVs and professional displays.
Each LED display technology has its own strengths and suitability for different applications, depending on factors such as brightness requirements, resolution, size, and viewing environment. The choice of LED display technology depends on the specific needs and constraints of the intended application.