III – Classification of LED chips
· MB Chip – definition and features
· GB Chip – definition and features
· TS Chip – definition and features
· AS Chip – definition and features
IV – Types of LED chip epitaxy
V – Element classification of LED chips
· LED chip model, light color, composition and wavelength relationship
LED is the basic electronic component for manufacturing various LED lighting fixtures, indicator lights, and LED screens. As an efficient and energy-saving light source, LED is widely used. So, as the core part of LED, what characteristics does the LED chip have? Now, let’s start with the development history of LED and learn about how LED works, and the classifications, composition elements, and luminous characteristics of LED chips.
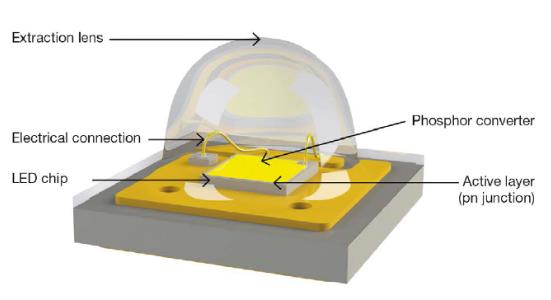
LED is the abbreviation of light emitting diode. LED is in fact a piece of electroluminescent semiconductor.
In an LED, the LED chip is housed in a wired frame and then sealed with epoxy resin. We often call these procedures as LED packaging, which is a type of solid packaging. The frame along with the epoxy resin give good protection for the internal components.
Therefore, an LED is solid and reliable, and excels in shock resistance.
In early 19th, we human beings had already recognized that semiconductors can generate light.
In 1962, Nick Holonyak Jr. of General Electric developed the first visible light emitting diode. That is also the first red LED in the world.
In the early times, LED was often used as an indicator for instruments and meters; later, with the emergence of various light color LEDs, LEDs were gradually used in traffic lights and large-area display screens (such as an LED screen), and produced good economic and social benefits.
For example, in the past, we could only use a low-efficiency 140-watt incandescent lamp as a light source to make a 12 inch red traffic light. In fact, the lamp itself can produce 2000 lumens of white light, but after passing through the red filter, the brightness get a loss as high as 90%, leaving only 200 lumens of red light.
But if we use red LEDs instead, we only need 18 pieces which consume only 14 watts of power with the same brightness as the 140 watt incandescent lamp can provide for the red traffic light.
There is no doubt that LEDs are more energy efficient solutions for traffic lights.
Kinglight 2727 lens LED for high brightness LED screen
As previously mentioned, LED is a solid-state semiconductor device that can directly convert electricity into light.
The core part of an LED is a semiconductor chip, which we often call it LED chip.
The LED chip is usually bond to the substrate of a metal frame, with one side as the negative pole, and the other side being connected to the positive pole of the power supply.
And usually we use epoxy resin to encapsulate an LED chip.
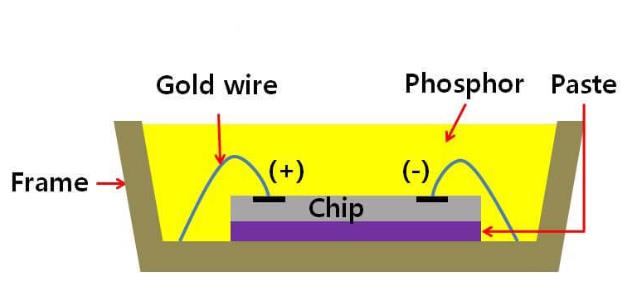
The LED chip consists of two parts, one is a P-type semiconductor, which is mainly composed of holes, and the other is an N-type semiconductor, which is mainly composed of electrons.
By connecting these two parts, we get a P-N junction inside an LED.
When electricity enters the LED chip through the bonding wires, the electrons in the N-type semiconductor will be pushed to the P region, where the electrons and holes recombine and emit energy in the form of photons, thereby generating light.
This is how an LED emits light.
In addition, the semiconductor materials that make up the P-N junction determine the wavelength of the light emitted by the LED; and the wavelength of the light determines the color of the light.
Furthermore, LED chips come in different types. The commonly seen types are the MB, GB, TS, and AS LED chips. Let’s see what they are and learn their features.
1. MB chips – definition and features
Definition:
MB stands for metal bonding, thus a MB chip is an LED chip based on metal bonding technology
In addition, MB chip is a patented product of UEC.
Features:
1-1. Using Si, a material with high thermal conductivity, as the substrateto provide efficient heat dissipation for the chip.
Thermal conductivity of different materials:
GaAs: 46W/m-K
GaP: 77W/m-K
Si: 125~150W/m-K
Cupper: 300~400W/m-k
SiC: 490W/m-K
1-2. The epitaxial layer and the substrate are bonded (wafer bonding) through a metal layer, while reflecting photons to avoid absorption by the substrate.
1-3. The conductive Si substrate replaces the GaAs substrate, has good thermal conductivity (thermal conductivity differs by 3~4 times), and is more suitable for the field of high drive current.
1-4. The bottom metal reflective layer is conducive to the improvement of light intensity and heat dissipation.
1-5. The size can be enlarged for application in high power fields, such as 42milMB.
2. GB chip – definition and features
Definition:
GB chip refers to a type of LED chip based on glue bonding.
It is also a patented product of UEC.
Features:
2-1. The transparent sapphire substrate replaces the light-absorbing GaAs substrate, and its light output power is more than twice that of the traditional AS (Absorbable structure) chip. The sapphire substrate is similar to the GaP substrate of the TS chip.
2-2. The chip emits light on all four sides and has an excellent pattern diagram.
2-3. In terms of brightness, its overall brightness has exceeded the level of TS chips (8.6mil).
2-4. The dual-electrode structure is slightly inferior to the TS single-electrode chip in terms of high current resistance.
Definition:
Transparent structure chip, a patented product of HP.
Features:
3-1. The chip manufacturing process is complex, much higher than ASLED.
3-2. Excellent reliability.
3-3. Transparent GaP substrate, does not absorb light, high brightness.
3-4. Widely used.
Definition:
Absorbable structure chip;
After nearly 40 years development, the LED optoelectronics industry has reached a mature stage in the research and development, production and sales of this type of chip. The research and development levels of major companies in this regard are basically at the same level, with little difference.
The AS chips we are talking about here refer specifically to UEC’s AS chips, such as 712SOL-VR, 709SOL-VR, 712SYM-VR, 709SYM-VR, etc.
Features:
4-1. Quaternary chip, prepared by MOVPE process, brighter than conventional chips.
4-2. Excellent reliability.
4-3. Widely used.
1.LPE:Liquid Phase Epitaxy, GaP/GaP
2.VPE:Vapor Phase Epitaxy, GaAsP/GaAs
3.MOVPE:Metal Organic Vapor Phase Epitaxy, AlGaInP、GaN
4.SH:GaAlAs/GaAs Single Hetero structure, GaAlAs/GaAs
5.DH:GaAlAs/GaAs Double Hetero structure, GaAlAs/GaAs
6.DDH:GaAlAs/GaAlAs Double Hetero structure, GaAlAs/GaAlAs
LED chip composition:
LED chips are mainly composed of several elements such as arsenic (AS), aluminum (AL), gallium (Ga), indium (IN), phosphorus (P), nitrogen (N) and strontium (Si); the specific composition varies depending on different application purposes and technical specifications.
Classification of LED chips:
1. According to the brightness of light:
1-1. General brightness: R, H, G, Y, E, etc.
1-2. High brightness: VG, VY, SR, etc.
1-3. Ultra-high brightness: UG, UY, UR, UYS, URF, UE, etc.
1-4. Invisible light (infrared): R, SIR, VIR, HIR
1-5. Infrared receiving tube: PT
1-6. Photoelectric tube: PD
2. According to the composition elements:
2-1. Binary chips (phosphorus, gallium): H, G, etc.
2-2. Ternary chips (phosphorus, gallium, arsenic): SR, HR, UR, etc.
2-3. Quaternary chips (phosphorus, aluminum, gallium, indium): SRF, HRF, URF, VY, HY, UY, UYS, UE, HE, UG
LED chip model, light color, composition and wavelength relationship:
| LED Chip Model | Light Color | Composition | Wavelength (nm) |
| SBI | blue | lnGaN/sic | 430 |
| HY | super bright yellow | AlGalnP | 595 |
| SBK | brighter blue | lnGaN/sic | 468 |
| SE | high bright orange | GaAsP/GaP | 610 |
| DBK | brighter blue | GaunN/Gan | 470 |
| HE | high bright orange | AlGalnP | 620 |
| SGL | turquoise | lnGaN/sic | 502 |
| UE | brightest orange | AlGalnP | 620 |
| DGL | brighter turquoise | LnGaN/GaN | 505 |
| URF | brightest red | AlGalnP | 630 |
| DGM | brighter turquoise | lnGaN | 523 |
| E | orange | GaAsP/GaP | 635 |
| PG | pure green | GaP | 555 |
| R | red | GAaAsP | 655 |
| SG | standard green | GaP | 560 |
| SR | Brighter red | GaA/AS | 660 |
| G | green | GaP | 565 |
| HR | super bright red | GaAlAs | 660 |
| VG | Brighter green | P | 565 |
| UR | Brightest red | GaAlAs | 660 |
| UG | Brightest green | AIGalnP | 574 |
| H | High red | GaP | 697 |
| Y | yellow | GaAsP/GaP | 585 |
| HIR | infrared | GaAlAs | 850 |
| VY | Brighter yellow | GaAsP/GaP | 585 |
| SIR | infrared | GaAlAs | 880 |
| UYS | Brighter yellow | AlGalnP | 587 |
| VIR | infrared | GaAlAs | 940 |
| UY | Brightest yellow | AlGalnP | 595 |
| IR | infrared | GaAs | 940 |