LED displays, also known as LED screens or LED panels, are electronic visual display devices that use light-emitting diodes (LEDs) to display information, images, videos, or other visual content. Here is some basic knowledge about LED displays:

LED screen plays important roles in stages, concerts, events, etc.
LED Technology:
LED displays are based on light-emitting diode technology. LEDs are semiconductor devices that emit light when an electric current passes through them. LED displays use an array of these LEDs to create a visible display.
Pixel Structure:
LED displays are made up of numerous individual pixels, which are the smallest units of the display that can be controlled independently. Each pixel typically consists of multiple LEDs, usually red, green, and blue (RGB), or sometimes just a single color LED.
Pixel Pitch:
Pixel pitch refers to the distance between adjacent pixels and is measured in millimeters (mm). Smaller pixel pitch values indicate a higher pixel density, resulting in a higher resolution and sharper image. LED displays with smaller pixel pitches are suitable for applications that require closer viewing distances.
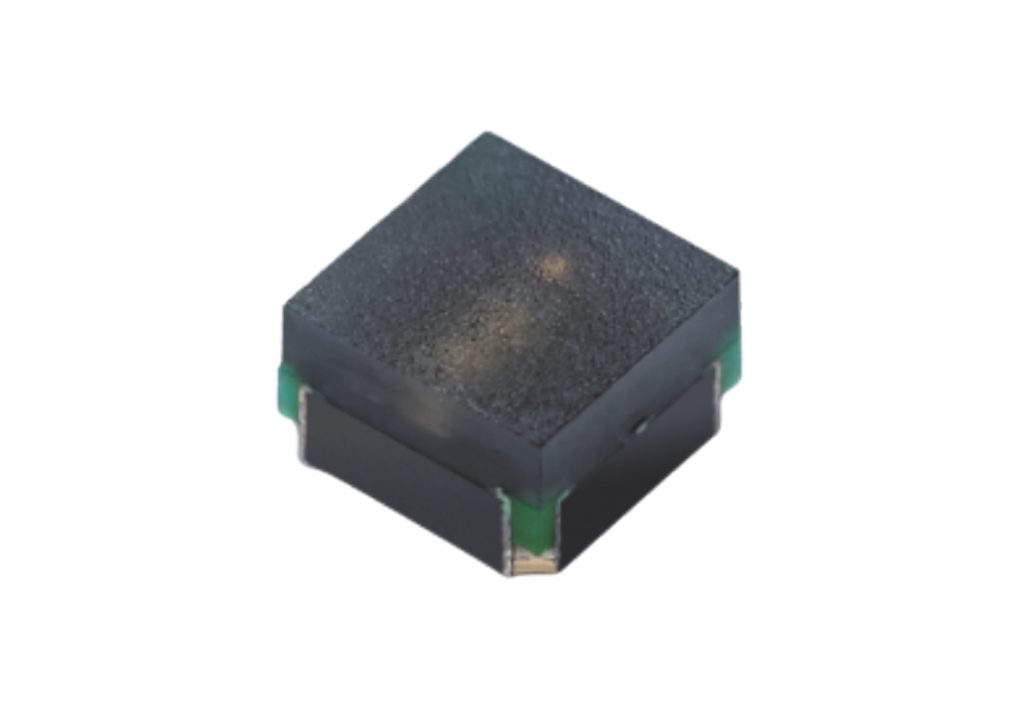
Kinglight MC0404N-M1 LED display lamp can make P0.6 LED display, which has a 0.6mm pixel pitch.
Resolution:
The resolution of an LED display refers to the number of pixels it has horizontally and vertically. It is typically denoted as the number of pixels per row by the number of pixels per column, such as 1920×1080 (Full HD) or 3840×2160 (4K Ultra HD). Higher resolutions provide more detail and clarity in the displayed content.
Color Reproduction:
LED displays can reproduce a wide range of colors, thanks to the use of RGB LEDs. By varying the intensity of each color LED, the display can create a vast palette of colors. LED displays are capable of producing vibrant and saturated colors, making them suitable for various applications.
Brightness and Contrast:
LED displays are known for their high brightness levels, making them visible even in well-lit environments. The brightness of an LED display is measured in nits or candelas per square meter (cd/m²). Additionally, LED displays can achieve high contrast ratios, resulting in better differentiation between dark and bright areas of the content.
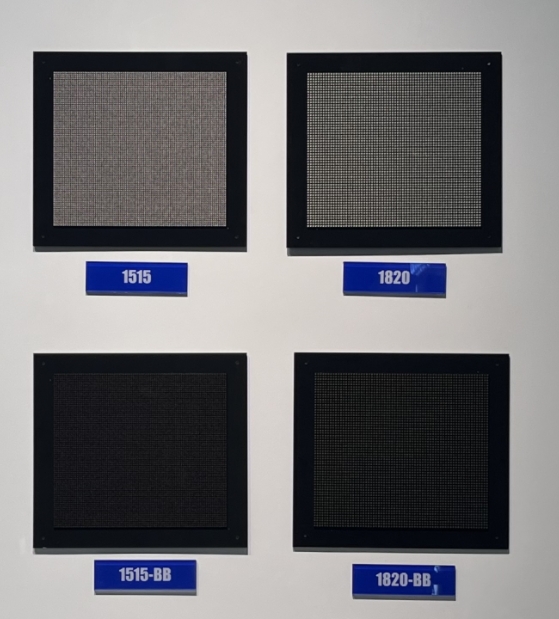
Kinglight LED display lamps with BB suffix in their product ID mean the LED chips are encapsulated with black surrounding for higher contrast and better visual perception.
Viewing Angle:
LED displays typically offer wide viewing angles, allowing the content to be seen clearly from different positions. This is an important consideration for displays that will be viewed from various angles or in large venues where viewers may be scattered across the space.
Control Systems:
LED displays are controlled by dedicated control systems, which receive input signals and convert them into instructions for the display. These control systems can handle various input sources, such as video signals, computer graphics, or multimedia content.
LED displays are widely used in various applications, including digital signage, advertising displays, stadium screens, scoreboards, indoor and outdoor displays, retail displays, control room displays, and more. They offer flexibility, high visibility, and the ability to showcase dynamic and engaging content.