Audiovisual systems play a crucial role in stage productions, enhancing the overall experience for both performers and the audience. Here’s an overview of the common audiovisual components found in stages.
Microphones:
Used to capture audio from performers, instruments, or other sound sources. Different types of microphones, such as dynamic, condenser, or wireless, may be employed.
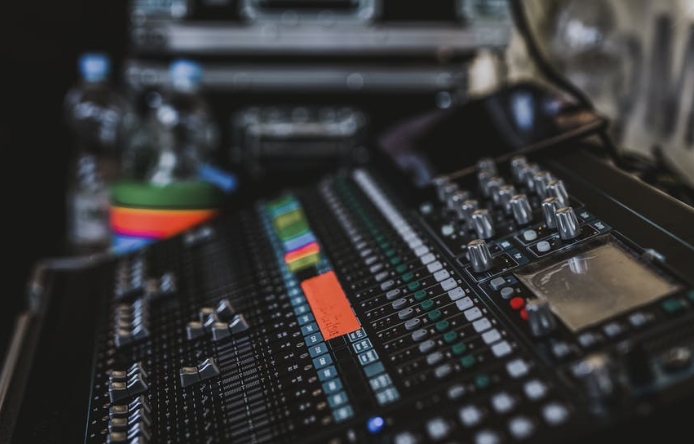

stage production-sound reinforcement system
Mixing Console:
Allows the sound engineer to adjust and balance the audio signals from various sources, controlling volume, tone, and effects.
Amplifiers and Speakers:
Amplify and reproduce the audio signals, delivering sound to the audience. This includes main speakers, monitor speakers, and subwoofers.
Signal Processors:
Equipment like equalizers, compressors, and effects units are used to shape and enhance the sound quality.
Stage Lighting Fixtures:
Various types of lights, such as spotlights, wash lights, and effect lights, are used to illuminate the stage, performers, and set.

stage production-lighting
Lighting Control Console:
Allows the lighting designer to control the intensity, color, and movement of the lights, creating different lighting effects and scenes.
Dimmers:
Devices used to control the brightness of stage lights, allowing for smooth transitions and adjustments.
Lighting Trusses and Rigging:
Structures that hold and position lighting fixtures, often suspended above the stage.
Projectors:
Used to display images, videos, or visual effects onto screens, surfaces, or stage elements.
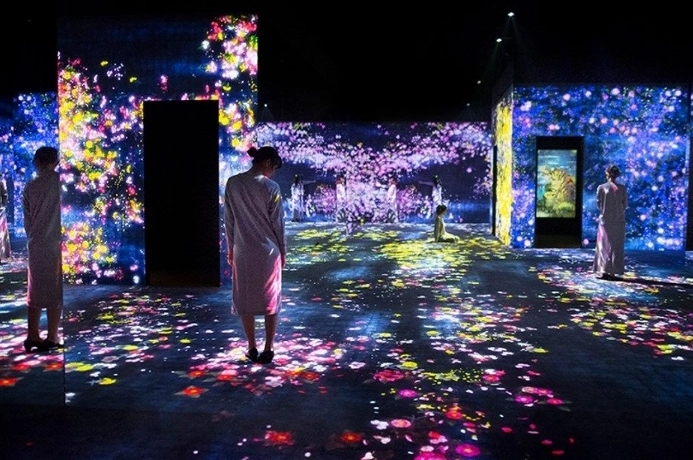

stage production – video projection
Screens:
Projection screens or LED screens can be used to display visuals or live video feeds of the performance.
Video Switchers:
Allow for seamless switching between different video sources and content.
Media Servers:
Systems that store, manage, and playback pre-recorded video content or graphics
.
Video Cameras:
Capture live video of the performance, which can be displayed on screens or projected onto surfaces.
Special Effects:
This can include fog machines, haze machines, strobe lights, lasers, pyrotechnics, or other effects to enhance the visual impact of the performance.
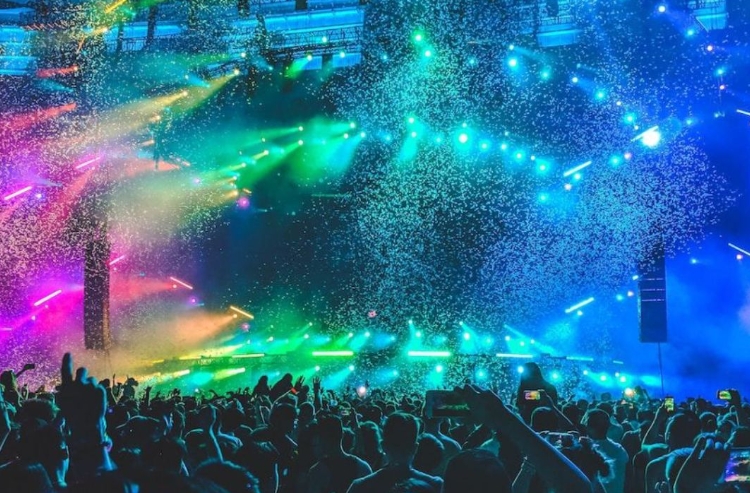

stage production-stage effects
Stage Automation:
Motorized systems that control moving parts of the stage, such as curtains, backdrops, set pieces, or platforms.
Interactivity:
Systems that enable interactive elements, such as touchscreens or motion sensors, which can trigger audio or visual responses.
Audiovisual Control System:
Integrates and coordinates the various audio, lighting, and video components, allowing for centralized control and automation of the entire system.
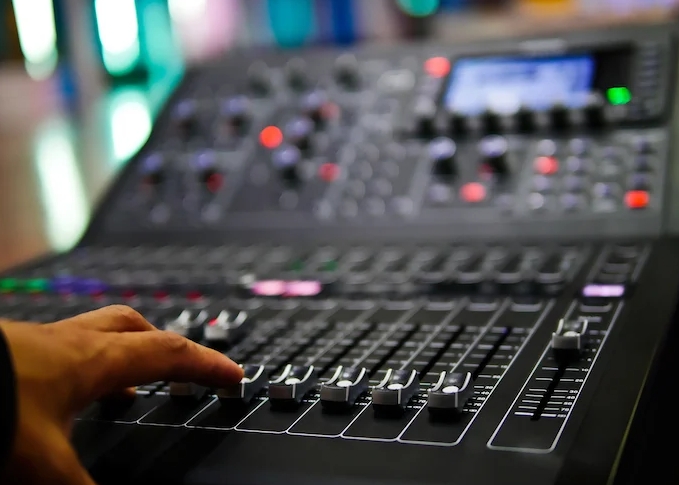

stage production-audiovisual control system
Stage Management Systems:
Communication systems used by stage managers to coordinate cues, timing, and communication between various production team members.
Kinglight 1820-KS3B LED – Kinglight offers a wide variety of LEDs for stage rental LED displays
These components work together to create immersive and engaging experiences in stage productions, ensuring high-quality audio, captivating lighting effects, and visually appealing video elements. The specific setup and configuration of audiovisual systems may vary depending on the size of the stage, type of performance, and production requirements.