LEDs are the most basic electronic components for manufacturing LED lighting fixtures and LED displays. They play decisive roles in the final performance of LED lighting fixtures and LED screens. In addition to the basic properties of LEDs, we should also know the some important performance indicators of LEDs. Now, let’s proceed to the following paragraphs and learn 12 critical features that indicate the performance of LEDs.
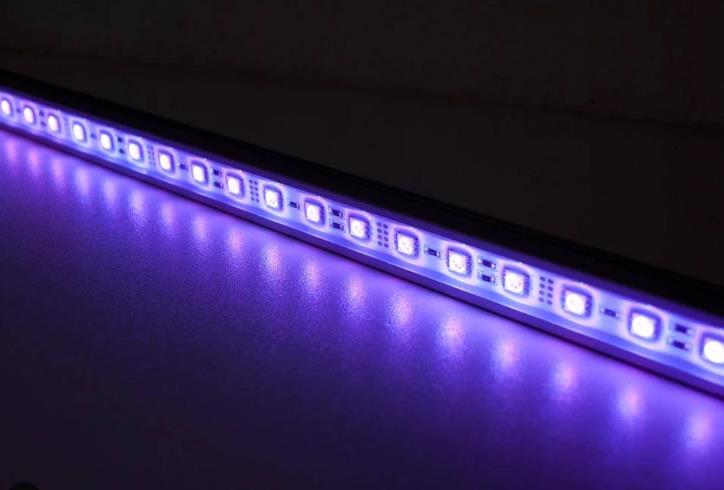

The light color of LED is a particularly important indicator, especially for LED lighting fixtures. Each LED must be clearly marked with the color of the LED. At present, LEDs for lighting fixtures mainly emits light in color of red, green, blue, cyan, yellow, white, warm white, amber, etc. Different LED colors will have very different related parameters of the product.
The forward limiting current (IF) of LED is generally 20mA, and the light decay current cannot be greater than 1/3 of IF, which is generally 15mA and 18mA. The luminous intensity of LED is proportional to IF only within a certain range. When IF is greater than 20mA, the enhancement of LED brightness cannot be distinguished by naked eyes. Therefore, the working current of LED is generally selected between 17-19mA. Of course, the above standards are mainly for ordinary low-power LEDs, that is, LEDs with a power between 0.04-0.08W. But for eagle eye LEDs, their working current may be as high as 40mA.
With the continuous development of LED packaging technology, high-power LEDs are constantly emerging. For example, the forward current limit (IF) of 0.5W LED is as high as 150mA; the IF of 1W LED is 350mA; and the IF of 3W LED can reach 750mA.
Of course, there are other high-power LEDs that also have higher forward current limit values, which you can refer to LED manuals to learn. And we won’t go into details here.
The forward voltage of the LED is the voltage when the positive pole of the power supply is connected to the positive pole of the LED and the negative pole of the power supply is connected to the negative pole of the LED.
The voltage is closely related to the color. For example, the voltage of red, yellow, and yellow-green LEDs is generally between 1.8-2.4V, while the voltage of white, blue, and emerald green LEDs is between 3.0-3.6V. It should be noted that the voltage of the same batch of LEDs will be slightly different, and it is necessary to refer to the data provided by the manufacturer in detail. In addition, when the external temperature rises, the forward voltage of the LED will decrease.
The reverse voltage of an LED is the voltage applied when the cathode of the LED is connected to the anode of the power supply and the anode of the LED is connected to the cathode of the power supply. The reverse voltage parameter of an LED generally refers to the maximum reverse voltage allowed to be applied; when the applied reverse voltage exceeds this value, the LED may be broken down and damaged.
The color temperature of LED is expressed in absolute temperature K, that is, a standard black body is heated. When the temperature rises to a certain degree, the color begins to change gradually from dark red – light red – orange yellow – white – blue. When a light source has the same color as the black body, the absolute temperature color of the black body at that time is the color temperature color of the light source.
Because the correlated color temperature is actually the evaluation value of the light color performance of the light source when the black body radiation is close to the light color of the light source, it is not an accurate color comparison. Therefore, two light sources with the same color temperature value may still have some differences in the appearance of light color. Color temperature alone cannot understand the color rendering ability of a light source for an object, or how the color of an object is reproduced under the light source.
The luminous intensity is another important performance indicator of LEDs. We usually describe luminance intensity in candela (cd).
The luminous intensity of LED is closely related to its application scenario. The light intensity of a single LED for indoor use is generally 500 microcandela (μcd) to 50 millicandela (mcd), while the light intensity of a single LED for outdoor use should be 100 millicandela (mcd) to 1000 millicandela (mcd), or even higher. This difference is mainly due to the different requirements for light brightness and illumination range in indoor and outdoor environments. For example, LEDs used outdoors require higher luminous intensity to ensure that they can still maintain sufficient brightness at a long distance or over a large area.
Kinglight – professional supplier of LEDs for screen manufacturing
Continue to read the topic:
12 Critical Features You Should Know about LED (II) >>>